It is important to make clear from the beginning that there is no single valid method to do an SEO Audit, so we must have an open mind to learn from other professionals and incorporate interesting aspects into our own methodology, since SEO is learning and constant review of the postulates and theories themselves.
Having said that, I will try to contribute my definition of what an SEO Audit is.

What is an SEO Audit?
It consists of the step-by-step analysis of each and every one of the SEO aspects or factors that affect the positioning of a web project, to prepare a diagnosis as accurate as possible and detect errors, problems, difficulties and SEO opportunities and thus be able to execute improvements in the future with the aim of positioning.
In SEO there is not a single valid way of doing things, that is, each professional or agency has its own method of analysis. However, an SEO audit must cover all the main aspects and key factors that affect positioning.
There is some consensus within the SEO world about which are the most important positioning factors, although in some aspects there may be different points of view, hence there are different methods.
How to do an SEO Audit step by step?
SEO Audit must carefully analyze all the factors that affect positioning, always from the point of view of who performs it, as a result of their experience and their vision of SEO.
Taking this into account, and following our criteria, we can group the Audit process into 5 phases or major main blocks of analysis:
- Indexability / Tracking
- Content / Keywords / CTR
- Inbound Links / Domain Authority
- Performance / Adaptability / Usability
- Code and Labels
📝 Block 1 of Analysis: Indexability and Tracking
Phase 1, Indexability and Tracking, comprises of the following important points that must be analyzed:
1. Indexability
The analysis of the URLs of the site that are indexed, that is, that can be served by the search engine as a result of a search, or in a less orthodox way, the pages of a website that appear in Google.
This first factor is very important. A website must always have its SEO – relevant URLs indexed, that is, those on which there is a real search intention and that have been optimized with the intention of appearing ranked for such searches.
Continuing along this line, it is just as important that the relevant URLs are indexed as that the non-relevant URLs are not.
Non-relevant URLs mean all those pages of a site that do not provide relevant information for a specific search intention or that have not been optimized for SEO, or that offer poor content (thin content) or that have duplicate content with respect to other URLs of the site, which does not contribute anything new.
By crawling we understand Google’s reading process of the content offered by the URLs of a website. Google prefers not to crawl irrelevant URLs, thereby saving crawl time that you can use to crawl other relevant URLs.
In the case of very large websites, from around 10,000 URLs approx. Google might have trouble seeing all the URLs and indexing them, due to the limited crawling budget or Crawl Budget.
This makes it even more necessary for you to spend some time analyzing potential crawling and indexing issues and solving them once you discover the reasons why URLs are or are not crawled or indexed.
Reasons why a URL might not be indexed:
- Noindex meta robots tag , marked within the web code or on platforms such as WordPress through plugins such as Yoast SEO or similar. In this case, the search engine tracks the content but does not index it, following the indication of the meta tag.
- Order Disallow in robots.txt. This indication in the robots file tells search engines which URLs or directories on a website should not be crawled.
- URLs with duplicate / irrelevant / poor content . Sometimes these pages of the site may not be indexed if the search engine so considers, despite the fact that they have no indication of type noindex or disallow.
- Orphaned URLs , that is, they do not receive any internal link and therefore Google could skip them when crawling and indexing. This does not always happen and depends on each specific case, but in general if a URL is important to you and you want to index and position it, you should link it internally.
As you can see, even though you think that all your important content is correctly indexed by Google, sometimes it is not so and it is very important that you analyze it and find solutions as one of the first actions to be taken in SEO Audit.
How to analyze the indexing status of a website?
You can view URLs that are indexed or non-indexed, valid, or have indexing issues, with the Coverage functionality of Search Console.
The free Google tool is an excellent option due to its simplicity of use and, at the same time, its reliability and detail when it comes to detecting indexing problems and evaluating possible causes in order to solve them.
Another option to see the indexed URLs of a site is to enter the command site: domain in Google. This way you can see the (approximate) number of URLs that the domain shows in Google and you can also see how SERPs or search results boxes are shown to users.

🛠 Another excellent (although paid) tool for analyzing the status of your URLs is Screaming Frog. With this tool, you will not only be able to see if the URLs are indexable or not, but you will also be able to obtain a lot of very valuable and detailed technical information about each of the URLs of a project.
💡 Remember: Do not forget that a website should not have all its content indexed in search engines, but only that which offers an answer to a search intention and is optimized for SEO, avoiding duplication problems, thin content, poor optimization, etc.
2. Robots
As I mentioned above, the robots.txt file serves to give search engines orders about which parts of the site should be crawled or not. It does this using the Disallow command, and then a relative URL of type /directory or /URL.
You can also add the Allow command to allow access to certain zones or URLs as an exception to a disallow.
The robots file can also be used to define the exact location of the sitemap to make search engines easier to work with.
In the SEO Audit, you must verify that a robot file exists and that it is correctly configured, depending on the site areas that must be blocked or allowed for crawling, according to the needs of the project in terms of indexing, crawl budget, pages, content duplicate etc.
How to view and analyze the robots.txt file?
You can see the robots on any web page by typing the domain/robots.txt URL. It is a file that is visible to the search engine and also to the users, with which you can easily analyze it even if you do not have access to the project backend.
3. Sitemap
The XML sitemap file must contain a list of the indexable URLs of the site to facilitate Google crawling and indexing, avoiding errors when indexing and speeding up crawling time, which can benefit the accessibility of your project by search engines and optimize your crawl budget.
For this reason, it is recommended that all websites, especially the most complex ones with a large number of URLs, have this file available and added by Search Console so that search engines can read it.
The site URLs must contain the relevant URLs that you wish to index, not those that are irrelevant or do not offer content for a specific search intention.
There are several ways to organize the sitemap index for search engines: it can be classified by content types (pages, posts, products, etc.), listed by dates, by areas of the web, by priority or newer URLs, etc.
The important thing is that it is understandable for the search engines and that it does not have errors in the list of URLs that it shows, i.e., the relevant URLs are always there and irrelevant ones do not slip through.
How to view and analyze the sitemap file?
You can see the main sitemap file at the domain/sitemap_index.xml URL. In this location is the index of all the sitemaps you have for the domain.
🛠 If instead of checking the existence of these files by hand you prefer to do it through an application that gives you a simple and quick report, you can use the free SEOptimer tool, which allows you to check in a moment whether a website has the sitemap available, so such as the robots file and many other basic elements for the SEO of a website.
📝 Block 2 of Analysis: Content/Keywords/CTR
Phase 2 comprises of the following key aspects of analysis:
1. Content
The content is a key factor in SEO to be analyzed thoroughly to detect potential problems and optimize it to the maximum.
Some of the most important aspects of SEO related to the quality of the content and that must be analyzed are the Value that it contributes, the Retention, Permanence and Loyalty of the user, the Scannability, the Duplicate text and the Cannibalization between URLs.
In addition, in this block, we will also analyze the strategy of Keywords, Architecture, Internal Links, 404 Errors, Broken Links, Redirects, URLs and Image optimization.
Value
The value that the content contributes to the user, that is, the level of satisfaction that the user obtains when consuming the content to cover their specific needs expressed through the search.
When the content is perceived by the user as value, it usually performs positive actions for the SEO of the site, such as placing links naturally (essential for SEO), staying on the page and visiting other URLs, sharing on social networks, adding comments, recommend it to other users, etc.
This is a somewhat subjective factor since there is no tool that directly measures the value of a URL, but you can measure factors such as residence time, bounce, links, shared on networks, positive comments from users, etc.
💡 Remember: Put yourself in the shoes of your user and think if the content you have created is the best possible that you could offer or if, on the contrary, it is one more content that does not stand out too much compared to others. If you are going to attack a keyword and if that keyword is also very competitive, try to create the best content that exists.
Retention, permanence and loyalty
The degree of interest and satisfaction that the content can generate in the user to make them stay on the page as long as possible and consider the content as ideal.
The more value you bring to the user, the more chances that they will stay on your page and even come back another time, generating more recurring visits in the future and preventing the bounce rate from increasing.
🛠 To analyze the degree of optimization of these factors, you have Google Analytics, which will provide you with exact data on how users interact with your content (residence time, bounce, etc.).
Scannability
The ease offered by the content to be read and understood by the user in a quick first reading, prior to a more detailed subsequent reading. It is important that this quick first reading the user can read and see the essential and valuable content.
If we place texts and hierarchical elements in a larger size and visibility compared to the rest, in that first reading the user will be able to understand and assess whether the content is going to be of value for them to stay and read it.
In those visible and large elements, you should place messages that bring interest to the user and make him make the decision to stay on your content. In other words, it is not only about adding value, but also reinforcing the appearance of value so that its value is evident to the user.
Duplicate
That the content is not literally duplicated or coincidental in a high proportion with other content external to the web or between the internal URLs of the web itself.
Google considers duplicate content as undesirable, that is, it prefers not to index the same content in many URLs so that each one contributes value by itself and thus not have to show users the same content in different URLs, thus like not having to crawl URLs with very similar content to save extra cracking efforts.
Duplicate content is sometimes involuntary, that is, it is not always the result of you consciously creating similar or equal content, but it can also be due to:
- Pages that group URLs with taxonomic or thematic criteria (category pages, tags, etc.)
- Pages automatic on a list of items that will not fit all in one page and distributed paging sequences
- URLs with parameters of any type that are the same as the original URL and are not redirected
- Not having the different versions of the domain redirected (domains that show the same under www or without www, http and https versions that show the same information as they are not redirected to the secure version, etc.)
How to fix duplicate content?
- Generating different content (in all those URLs that are real target of positioning and work different keywords)
- Unindexing duplicate URLs if they are not necessary to the position since they usually work the same keyword (cannibalization)
- Using canonical to indicate to the search engine which is the main URL to index and to prioritize among a set of similar URLs
- Using next and prev attributes in-page URLs.
🛠 With the free Siteliner tool you can easily analyze if there is internal duplicate content on the website.
Cannibalization
It is important that there is no more than 1 URL to work the same search intention on the site. That is, each search intention or keyword must be worked on a different URL of the site so that Google understands well which URLs serve each search intention so that you can position better.
Also, if you group a whole global search intention (keyword and its related words) in a single URL, all the authority, links, network shares, traffic, etc., you group them in that single URL, instead of dispersing them in several, which makes it easier for you to achieve your positioning objective.
Optimization of content (labels, density, etc.)
In this section we analyze if the content complies with the correct structure of h-head tags, i.e., the content is structured following a logical format of h1 or title 1 for the main title, titles 2 or h2 for the subtitles or epigraphs main, titles 3 or h3 for the sub-headings, etc.
It is assumed that in these header tags or titles h we are going to put enough relevant words of the content (keywords and related words), which is beneficial for Google to understand that those words are important.
The <title> tag is also super important, which is normally the one that contains the title (and the keyword) and that usually coincides with the title of h1, although not always. This is the most important tag of all in terms of relevance to Google. Also, what you put in the title then appears as a title in the Google search results box (SERP).
Organizing content in this way is not only good for the correct understanding and scannability by the user, but also for Google, since the title tags and the texts you include within them are relevant to the search engine.
In addition, we must analyze the density of keywords within the content, that is, the total number of times the key expression appears written against the total number of words in the content. Keyword density should not be very high and should tend to be natural, to avoid falling into Keyword Stuffing.
Apart from these, there are other tags that you can add to your content to optimize SEO and improve how it is shown to users on other sites besides your website, to increase clicks and traffic. They are the social graph tags (open graph and twitter cards), which control how your content appears on social networks (images, titles, descriptions, etc.). You can add them with the Yoast SEO plugin.
You can also add Rich Content Tags or Rich Snippets from Schema.org, which optimize the appearance of SERPs in Google with additional content, which can increase your CTR (Click Thorugh Rate).
Be careful, don’t forget that Google can only read content written in text format. Texts painted on images, multimedia elements such as video or audio, Slideshare presentations and other elements of this type will not be read by Google along with the rest of the page content. For this reason, always think about the possibility of transcribing into normal text format and readable by Google.
💡 Remember: The times are over when to position a keyword you had to repeat it over and over again within the content. Google values naturalness more and more every day . Write naturally, without thinking too much about repeating the keyword and without forcing anything, using lexical richness and synonyms. That is, write for the user and you will be writing for Google.
Architecture
The architecture web is a very important factor. The way in which a website structures its sections and groups its URLs, the depth of directories in which the URLs are located, how the information of the site is hierarchized, etc.
How does web architecture affect SEO? Its incidence is studied from two planes: on the one hand, it influences the user’s understanding and ease of browsing the web, and on the other, the way in which search engines crawl and understand the site.
Web architecture not only works on a structural level, but also on a semantic level. That is, the keyword research and the key terms that are going to be worked on the site can determine to some extent its structure and organization.
When you analyze the web architecture in SEO Audit, make sure that the site is well structured according to usability criteria and also semantics.
The important sections, either because there is a broad search intention or because they are a priority positioning objective, are usually placed in main menus and upper areas, they are usually very internally linked and they are usually a few clicks away (and not very deep in the directory tree) from the home page.
It is recommended that on the website the information relevant to SEO is not more than two or three levels of clicks from the main domain, that is, do not put the relevant content in URLs of the type domain.com/directory/directory/directory/slug-of-content. This will favor tracking and obtaining internal link juice.
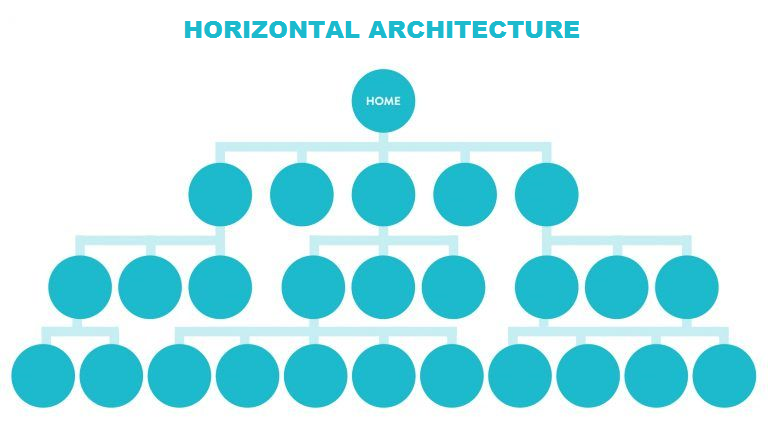
Below you can see an infographic that shows a typical web structure with well-organized horizontal architecture with a maximum of 3 levels of navigation.
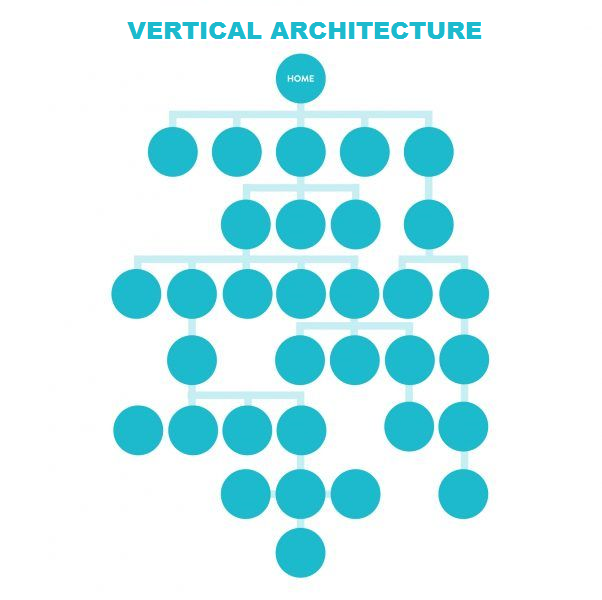
Here is an example of vertical architecture, less organized, with too many levels of navigation and even some orphan URL (not internally linked).
Usually, the websites have been built following somewhat arbitrary or capricious criteria according to the will or personal taste of the client or the developer. This is common when developing a project without the figure of an SEO from the beginning making architectural suggestions.
When this happens, it is necessary to carry out a global review of the web with SEO criteria and to restructure all the content and sections.
🛠 You can easily analyze the web architecture and its directory structure with Screaming Frog, using the Visualization> Directory Tree Graph functionality.
Internal links
The internal linkage is an important factor ahead of the SEO and must also be analyzed in the audit as an essential aspect for good positioning. Internal links convey authority between internal site URLs.
It is recommended to encourage internal linking to give strength to the areas you want to be more relevant within the site, sending link juice to the URLs you want to reinforce.
As we have seen above, internal linking is also part of the web architecture and helps to organize and distribute the internal authority of the web, as well as to facilitate search by the search engine.
In addition, it benefits the decrease in the bounce rate by recommending the user other URLs of the site to visit.
🛠 To analyze the internal linking of a website you can use tools such as Search Console (free) or Ahrefs (paid).
404 Error
In the audit you must analyze the 404 errors that your website has. But, contrary to what some believe, 404 errors are not penalizing or generally as troublesome as you might think.
What is a 404 error? It is a URL of the site that no longer exists or is incorrectly written in an internal link or poorly linked from another website, so that instead of content, what you see is a 404 status page.
The reasons that you have a 404 error can be: you have deleted or changed a URL, they have been linked externally incorrectly from another site, or sometimes you may have a plugin or application installed on your website that generates URLs from dynamically disappear when you uninstall them.
The main problem with 404 errors is that there are relevant URLs on the site that users cannot see, such as important site content, service or product pages, landing pages, etc. In this case, the user could be frustrated by not being able to see the content and, as a consequence, leave the site, not buy your product or contract your service, not share, not link, not comment, not recommend. In short, if there is no content in the URL, there is no user interaction or conversion or benefit for your brand.
Another possible problem, in the case of websites with many URLs, is that you have many internal links to pages with error 404, which would force the search engine to consume crawl budget unnecessarily. In other words, you would lose tracking time following internal links that lead to error pages.
How to fix 404 errors?
Just do 301 redirects from the error URLs to the URLs of the site you want. Generally, towards the equivalent or similar URLs, or failing that to the home page. It is important to note that it is not necessary to redirect all 404s. Only the relevant ones, that is, those that are generated by pages of the site that previously existed and that had certain page authority, links, shares, traffic, etc.
🛠 You can monitor 404 errors with tools like Screaming Frog (paid) and Ahrefs (paid) or Search Console (for free).
Broken links
The outgoing broken links (links from the site pointing to another site and that do not work because they have been mistyped or because the web or destination URL no longer exist) are negative for the user (because they can not access the link giving an image of little care) and for Google (since it conveys the idea that the site is poorly optimized and provides poor quality).
Also, just in case there are a lot of broken links, it makes you waste time tracking links that are useless, and this can affect the crawl budget.
Linking to relevant and similarly themed sites are positive for Google because it helps them to track and also adds value to the user, therefore it is a factor that you must take care of and of course analyze it in the audit.
🛠 To detect broken links on a website, you can use a free tool called Broken Link Check that works very well for this analysis.
Redirects
The most typical redirects are 301 (permanent) and 302 (temporary). A redirect is used to send user traffic from an old URL that no longer exists to a new one. The redirect, if permanent, also transfers authority from the old URL to the new URL.
In the SEO Audit, we analyze the redirects that the web has implemented both at the domain level (complete redirects from an old domain to a new one) as well as specific URLs (pages or entries that no longer exist, products, etc.).
When we make redirects we can slow down the loading of the web by forcing the browser to reload another URL, or even several if they are chained redirects. Obviously, the incidence in loading time is only relevant to SEO if it involves many redirects or there are specific problems in those redirects at a technical level.
It is recommended to make redirects with the htaccess file on the server, since they are the ones that consume the least resources compared to other types of redirects with Javascript, HTML, etc.
Another important aspect of redirects is that they are made to the correct URLs, taking into account that with redirects you transfer authority from one to the other.
🛠 You can analyze the redirects with the Link Redirect Trace extension for Chrome, or the HTTP Status application that returns all the status codes that a specific URL has.
URLs
In the URLs section we are going to analyze if the URLs are friendly and include the keyword of each page that we want to position.
Every URL on every page on the site has a slug. The slug is the part of the URL that follows the domain. In the example URL example.com/slug, the slug is what follows the domain.
It is recommended for positioning that the slug is friendly, i.e., it includes the keyword, word or key expression (separating the terms by means of hyphens) around which you are going to want to position each page of the site and that it does not include characters strangers, numbers, stop words like articles, conjunctions, etc. It is also recommended that they tend to be short.
Images
How to know if the images of a site are optimized for SEO? The images are optimized, on the one hand, in terms of size and weight. On the other, regarding its semantics.
The first of the optimizations aims to streamline the weight of the image by subtracting an unnecessary resolution to be seen on screens. A medium-low pixel-per-inch quality is usually sufficient. Also, size is important. If an image is going to be viewed on your page at a size of 300 × 300 pixels in width and height, upload it to that exact size so that it weighs less.
As for the second aspect, it is necessary that the image includes text data that can be read by the search engine, since today the texts overwritten in the image are not yet taken into account by Google.
The text fields that you can include in the images are title, alternative text (alt) and description. The first two are relevant and it is recommended that you include the image and keyword description. The description is used to display a short text in the search results box next to the image.
Another aspect that helps is the name of the image file . If this name includes the keyword next to the file extension, you are providing more data to the search engine and therefore favoring that it can be positioned based on that keyword.
The context of the image, that is, the text around the image within the content, can also help you. It is easier to position an image that is inserted within a text related to its theme than an image URL without anything else.
🛠 As in many other factors, the Screaming Frog tool can be used to analyze how optimized images are for SEO, i.e. if they include these necessary text labels to position. To see if the images are optimized in terms of weight and size, you can use GTMetrix, which provides infinite performance data of the elements of a web page.
2. Keywords
What keywords does the project currently position or try to position? Are they correct according to the company’s objectives and the current possibilities of the project or should I be trying to position others? What keywords does the competition rank?
Focusing SEO actions around the right keywords is crucial. If you are trying to position the wrong keywords, irrelevant to your business, too difficult to position or with insignificant search volumes, you are probably spending time and resources for nothing.
Therefore, it is of paramount importance that before developing your content plan and even before structuring the architecture of your website, you do a thorough Keyword Research in which you obtain the appropriate keywords to position your project.
From this, you must develop your future content strategy and organize your website with main sections and articles based on the correct keywords.
A web project that has not previously performed a keyword search may not rank any relevant term or does so accidentally, denoting poor strategy and possibly yielding few results.
As I have already mentioned in the optimization part of the content, once you have found the keywords you must distribute them among the URLs of your site following logical criteria for the user and also SEO architecture. And always keeping in mind that each indexed URL of the site must work a keyword or search intention separately, to avoid cannibalization.
How to optimize your keyword within the content to improve SEO?
- Write naturally, do not force repetitive typing of the keyword
- However, write with a certain keyword density, and place it in relevant places on the page (titles, h headings, alt, anchor texts, first paragraphs, etc.)
- Write a minimum amount of content at least, they say 300 words but even if you can write more, do it. The key is to satisfy the user’s demand for information, not simply reach a previously stipulated number of words.
- Write synonyms of the keyword throughout the content, because although they may seem different keywords, they actually respond to the same search intention and probably also have certain search volumes, because although they are less searched than the main keyword, some users may use them.
🛠 With Keyword Density Checker you can also measure its density within the content, that is, the percentage of times the keyword appears compared to the rest of the words in the content.
3. CTR
The CTR (Click Through Rate) or clicks you get in Google regarding the total number of times your printed result comes out, is a very important factor that of course has to be analyzed in the SEO Audit, since it has a crucial impact on positioning.
If you detect that your results (SERPs) have a low CTR, you should ask yourself if they are attractive and explanatory enough to attract the attention of users and receive clicks.
There are studies that make approximate averages of how much CTR is reasonable depending on your position. Although this obviously varies depending on the sector (competitors that exist, user behavior habits, etc.) and the types of results that Google displays for the query.
Nowadays Google is already showing outstanding results that throw down the first results that were previously seen at the top. There are also results in map formats, rich snippets, etc., which in some cases greatly change the rules of the game.
Suppose, in your sector, the normal result is that the third result achieves an average CTR of around 15%. In that case, you should analyze if your results that are in that position are receiving the adequate or minimally acceptable CTR.
How to improve the CTR of your results (SERPs) in Google?
- Place very attractive titles with valuable words and calls to action for the user, using all the available extension
- Write engaging and also highly explanatory meta descriptions about the value of content.
- Use attractive and prominent visual elements in your titles and meta descriptions, to attract the user’s attention, such as emojis, special characters, etc.
- Use elements rich (rich snippets) whenever possible, to provide a more specific and specialized content to the user and also visually highlight (snippets of recipes, events, articles, reviews, star ratings, etc)
- Remove the dates if your content is evergreen or timeless, to prevent the user from thinking that it is obsolete content and prefer not to click on you.
- Use copywriting techniques that work and that have been contrasted by other professionals.
- Test, analyze, observe, try again and again changing your own SERPs until you find the most suitable formula for the particularities of your sector.
- Look at the SERPs of the competition and be inspired by what they do well (note, I did not say copy as is) and what they do wrong (not to repeat it).
- Arouse great interest with the texts of your SERPs, try to answer very clearly to a specific question or problem, be forceful and clear when expressing the value of the article (although without going too sensationalist).
- Offer valuable content that is perceived by the user as valuable, do not try to give a too commercial touch to the content that serves to provide pure value.
- Work on your brand image globally, create good content, be active on social networks, respond to blog comments, to generate a positive perception of your brand that users remember when deciding on what results to click.
🛠 With the Search Console tool, you can easily analyze your CTR for all the URLs of your web page.
📝 Block 3 of Analysis: Inbound Links/Domain Authority
In phase 3 analysis we will analyze inbound links (backlinks) and domain authority:
1. Inbound links
The inbound links or backlinks (links to get other websites to your website) are a crucial SEO factor forever and now, of course.
Since Google was born, the quality and quantity of the incoming link that a domain has, has been one of the most relevant and direct factors that Google uses to determine its position. Links transfer authority from one domain to another, or from one URL to another.
Therefore, it is important to analyze that your domain has a good number of inbound links of a certain authority, of natural appearance, of the do-follow type (those that transfer authority) although not all, and in general that conform a healthy link profile and references from as many possible relevant sites related to your topic.
It is important to monitor the profile of inbound links that the domain has, to assess the quality of the links, and also the health or appearance of naturalness of the same. An artificial-looking or toxic inbound link profile could be penalized by Google and harm your SEO.
Sometimes, especially if it has not been monitored before, the inbound link profile of a domain can be full of undesirable links, either due to random reasons, or due to external attacks, or due to a proper action to purchase inappropriate links.
Google says: “make your links natural.” This does not mean that Google can know that you have bought links, but it certainly does analyze your links to see if they are apparently natural or not.
You should have a certain diversity of dofollow and nofollow links, preferably from websites with a niche similar to yours and in the same language as your site, and obtained over time and not all at once, since this type of links are the most natural.
🛠 You can analyze your inbound link profile with the Search Console tool (free) or with Ahrefs (paid). Another free tool for monitoring links is Ranksignals.
The authority , relevance or popularity of the domain can be analyzed from different points of view and different tools. In general, a domain with authority is one that has good links, signs of good SEO and some age.
To assess the relevance of a domain, Google has always taken into account its own metric, PageRank . This value is impossible to know today, so there are other metrics or criteria to estimate the authority of a domain.
You can measure your domain with the Domain Authority of Moz, a fairly reliable metric to determine the health and quality of a domain. You can also use paid tools like Ahrefs, whose metric, Domain Rating or DR, is also quite reliable to estimate the quality of a domain.
However, you should bear in mind that these metrics are carried out by tools external to Google and are still estimates based on a series of criteria. Do not take these results as absolute, but rather as a rough indication of the current SEO status of the analyzed domain and its evolution over time.
📝 Block 4 of Analysis: Performance/Adaptability/Usability
Phase 4 will serve to analyze the performance and speed of the web (also called WPO, Web Performance Optimization), and how is its responsive adaptability for different devices, as well as its degree of usability or ease of use for users.
1. WPO
In SEO Audit we will also analyze the performance of the web page, that is, its loading speed. This is today an important factor that must be measured and optimized since Google has already made it clear that websites have to be fast and load without problems.
There is no maximum loading time that Google has defined, therefore the slogan is: it tries to make the web load as fast as possible, identifying and separating all the elements and components that, although they may be slowing down the speed, They are essential, and all those that are not so necessary and you could eliminate to gain speed.
There are numerous factors that can affect the loading speed of your website, which I will list and explain below:
What are the main factors that influence the loading speed of a website?
1. Hosting
The server where you host your website is one of the main factors that determine a fast or slow load. I recommend hosting your website in specialized hostings for your system or CMS, with good performance and security, as well as good support.
Changing from a bad or regular hosting to a good one is one of the simplest actions you can carry out to improve the loading speed of a website and that you can recommend to your client before carrying out other optimizations on their project.
Good hosting includes advanced features or improvements like Gzip compression, Keep Alive, advanced Caching systems, etc., which are excellent for improving performance.
2. Template and plugins
If you are using a content manager or CMS type WordPress or similar, it is also important what template or theme you use, as well as the plugins or modules that you add to the web to include extra functionalities. A slow template will make speed optimization very difficult for you, as well as using very heavy plugins or installing too many of them.
3. Images
Another simple aspect to detect and fix. Sometimes a website is slow because its images are not optimized in size and weight, and this is one of the essential actions that every web developer must take. Do not upload larger or higher resolution images than necessary. Regarding size (width and height), never upload images without first passing them through Photoshop or similar tools and leaving them at the exact size.
4. Cache
Installing a cache system is one of the most recommended methods to improve its performance and response speed. A cached web serves its static elements faster because they are already preloaded.
5. Use CDN
A CDN improves the delivery of your web data to the user thanks to the fact that it uses data centers spread over various geographic locations and all kinds of improvements to increase the speed of loading and the fluidity of the server response.
6. Minimize the code
Reduce the amount of code that your website has by cleaning unnecessary code or reducing the space it occupies through code minification, speeding up its reading by concatenating lines of code.
7. Asynchronous load
Loading certain elements of the page deferred avoids a bottleneck or bottleneck in the header of your website due to the excessive accumulation of requests to Javascript files and other types of files, by loading the elements shortly after the start of the charges without the user being able to perceive it but improving the initial charge speed.
8. Optimize the database
If you regularly clean the useless and obsolete tables and contents of the web database you will speed up the queries made from the web and in this way you will improve their speed. When you uninstall plugins, sometimes tables remain in the database, also when you make revisions or save your content.
9. Loading images and videos (Lazy Load)
Make sure that the images and videos do not load all at once but that they load progressively as the page is scrolled, avoiding overloading the initial load with too many multimedia elements.
10. Calls to external services
Avoid installing too many elements on your website, especially if many of them are superfluous or not really important. Keep in mind that you slow down your website every time you insert content from social networks, videos, plugins to connect with external tools or applications, code scripts to insert features on your site, etc.
11. Periodically review and update the website
Perform from time to time optimization and updating tasks of your CMS, your template and plugins, so that everything works perfectly, avoiding slowdown and security problems, as well as incompatibilities between the various components of your website, factors all of which sometimes can hinder the smooth loading of your website.
You can measure the loading speed of a web page with free and very complete tools such as GTMetrix, Pingdom Speed Test or Page Speed Insights.
2. Responsive adaptability
Google analyzes whether websites are responsive as a factor for positioning, and this has been the case for a few years now, with which in SEO Audit it is essential to also analyze how adaptable or responsive the website is.
In the SEO Audit, we are going to analyze if the web adapts correctly to each screen size and device (desktop, tablets, smartphones, etc.), not only because Google takes it into account, but also in the face of the user.
Don’t forget: Many SEO factors are optimized not only to meet Google’s guidelines but also for the user. Because the user, through their way of interacting with your website (residence time, bounce, CTR, etc.) is sending signals to Google about the suitability and value of that content, and this influences SEO because Google attends to these signals of the user to rank.
If the website is not responsive or not at all, there may be users who on certain devices do not have a satisfactory user experience, which could affect the time they remain on the website and the actions they take within it. how to interact with sections, generate conversions, etc.
Therefore, it is not only about having a responsive website (nowadays, any WordPress template or similar platforms already come with responsive versions implemented), but how well adjusted and optimized these responsive versions are. Sometimes, the template you have used to make your website has to be adjusted with CSS or plugins to make the responsive versions perfect.
How to analyze if a website is responsive?
You can do two things: one, monitor the web directly on real devices, observing with total precision how content behaves on that screen size. Or two, you can monitor it with desktop applications that simulate various screen sizes, brands and models of smartphones, tablets, laptops, etc.
🛠 You can monitor how a web page looks on various devices and screen sizes with the Google Chrome Inspect command, which lets you preview what your website would look like on a bunch of devices.
In addition to responsive adaptability as an SEO factor, it should be borne in mind that Google recommends implementing the AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) protocol that serves to further optimize performance on mobile devices, by reorganizing and cleaning web parts.
3. Usability and User Experience
The third point of this block 4 of SEO Audit is going to focus on usability and user experience, which although they seem the same, in reality, are not exactly the same concept.
What is usability?
Usability is the ability of a website (or any application) to be correctly understood and used by the user. In other words, a usable website is one in which the user knows how to use its functionalities as easily as possible and without serious problems of understanding, operation and navigation in the different areas of the site.
A usable website is intuitive and accessible to the user. It does not require too many explanations of use and navigation for the user to navigate through the menus and find what they need without problems. It has text in an easily readable size, font and color. It allows the user to understand the objective or purpose of the website since it offers understandable and coherent messages for the user. It loads fluently. It does not show interruptive or excessively invasive elements for the user. It can be browsed and understood the same on any device or screen size, whether it is on a desktop, tablet or smartphone. It allows a satisfactory user experience, and that benefits SEO because a satisfied user usually stays longer on the page and interacts more.
A non-usable website is poorly understood, not very intuitive and little accessible to the user. It can work abnormally or unexpectedly, load slowly, or make it difficult for the user to find the sections they want and the correct interaction with the menus, as well as any type of interaction with forms, buttons, web applications, etc. It makes it difficult for the user to understand the objective or purpose of the website since its messages are contradictory or poorly explained. It displays elements that interrupt navigation or that disturb the user. It has texts that are not very readable in small sizes or with poorly readable fonts, in little contrasting colors with respect to the background, with insufficient line spacing, etc. It does not behave correctly on all devices and screens.
What is the user experience?
The user experience refers to the degree of satisfaction or dissatisfaction previous usability factors generated on the user, prompting him to stay on the site, interact, perform positive actions for SEO and generate conversions if the site is usable, or the opposite if the site is not usable.
Therefore, if usability refers to how the web favors or not the use of the user, the user experience refers to how the web has positively or negatively impacted the user based on all those factors.
And consequently, positive user experience is beneficial not only for your brand image and your sales or conversions but also for SEO, since a satisfied user or who has managed to appreciate or understand the objective or value of the web, It usually generates better signals or clues that affect SEO:
- More time spent
- Less bounce rate
- More CTR
- More visits to internal pages
- Most shared or recommendations
- More form submission
- More natural links
- More conversions (leads, sales, etc.)
🛠 You can monitor the exact behavior of the user on the page with a tool such as Hotjar, where they click most frequently, see their entire recorded sessions, etc.
📝 Block 5 of Analysis: Code and Labels
Phase 5 analysis is related to all technical aspects at the code level, specific coding problems in the different languages or technical implementations that may be damaging or benefiting the SEO of the site.
1. Code and labels
In this section, we are going to analyze the project from a technical point of view. On the one hand, we are going to scrutinize the exit code of the web (the one that Google reads in the front public part of the web), basically HTML, Javascript and CSS code.
We will start with the most common language of all websites, HTML. The HTML code generates the visual structure of the web page, and also uses meta tags to send information to search engines and browsers, in addition to specific attributes within those tags.
Title
<title> </title>The most relevant tag of all and in which the keyword yes or yes must be , since it is also the title that appears in the results box that shows the URL in Google. It is at the top of the page code and you can see its content if you rest for a moment on the browser tab. It usually matches h1, but it doesn’t have to. Title is a meta tag (but not to be confused with the meta title tag that is no longer useful for anything!), That is, it is not visible on the page but is to be read by the search engine.
Meta Description
<meta name = "description" content = "">This tag defines the description that will appear in the Google results box, under the title. It does not have a direct importance in SEO (not by putting the keyword in the meta description you will reinforce it more directly), but it influences the CTR (Click Through Rate), with which you should optimize it for each URL you are going to index of the site. Optimizing it means: filling the 155 characters it offers you with an explicit, attractive and persuasive description of the content, using rich and visually prominent elements. It’s about winning the click against your competitors.
Headers or Titles
<h1> </h1>
<h2> </h2>
<h3> </h3>
<h4> </h4>
<h5> </h5>
<h6> </h6>The title tags h (h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6) serve mainly two things:
On the one hand, they visually hierarchically format the epigraphs of the content, showing them from largest to smallest size and thickness as it is lowered from the <h1> to the <h6> tag. That is, h1 usually looks very large because it contains the title, and h6 is usually the smallest (although it doesn’t have to, you could easily modify this with CSS). A hierarchical correct visual help make the content more scannable visually (the user can understand the content quickly, in a first reading scroll fast) and this can benefit the dwell time, rebound, conversions, etc.
On the other hand, h title tags have direct relevance in SEO (those with the most <h1> and those with the least <h6>), and it is recommended that you place important texts on them: keyword, synonyms for the keyword, etc. You can only have one <h1> tag per URL (in the title), then the content captions in <h2>, <h3> tags for subheadings, and so on downward in relevance up to <h6>.
Alt and Images Title
<img alt = "" title = "">The attributes alt and title serve so that Google (and also the user in certain cases) can understand the images semantically, that is, they are the texts that Google reads from the images. Therefore, in alt and title you must put a description of the image with keywords, so that it serves for the accessibility of the site and also for Google.
og: (Open Graph)
<meta name = "og: title" content = "">
<meta name = "og: description" content = "">
<meta name = "og: image" content = "">
<meta name = "og: url" content = "">
<meta name = "og: site_name" content = "">
<meta name = "og: locale" content = "">
<meta name = "og: type" content = "">Open Graph tags add valuable meta-information to social media and other platforms about your content. Using the Open Graph of image, title, description, site, etc., you can define how you want your URLs to look when they are shared on networks. That is, you can define the content that appears in the snippet automatically when someone or yourself publishes a web URL on networks (whether it is a post, a page, a product or anything else).
The contents of a website tend to generate more interaction and clicks from social networks if they are well optimized, with attractive titles, explanatory and persuasive descriptions, quality images, etc.
Lang
<html lang = "">The lang attribute of the general <html> tag is defined above the entire document, and is used to indicate the language in which the page is written. If the site has different language versions, this attribute should always declare the language of each URL.
Hreflang
<link rel = "alternate" hreflang = "">The hreflang attribute of the <link> tag declares, in the code of each page, which are the different language versions that a certain page of the site has, and also indicates which are the URLs where those other language versions of that page are located.
In this way, Google can perfectly understand the internal structure of the multilanguage site, to show each indexed URL in the correct language version of the search engine.
Meta Robots
<meta name = "robots" content = "" />The robots meta defines whether a specific page of the site should be indexed or not, and crawled or not (using the index-noindex, follow-nofollow values ). If you insert the index value in the content attribute, Google will index the URL. If you also enter the value follow, Google tracks and follows the link trail. Values are placed in comma-separated pairs, as follows: ” index, follow”, or “noindex, follow”, etc.
Canonical
<link rel = "canonical" href = "" />The link tag with canonical rel attribute defines the main singularity or relevance of a URL with respect to others that are similar or have similar content, or be part of a series of similar URLs.
Link Title
<a href="" title=""> </a>This attribute of the links <a> tag is used to provide additional information about the link, and Google tracks it as well, as does the anchor text. In both cases, using the keyword can be beneficial to enhance the positioning of the destination URL around that keyword.
Structured Microdata
The microdata structured each day are more SEO useful because help Google understand the content with high accuracy and thus to serve as a search result more appropriate and accurate for the search.
The benefit is twofold: on the one hand, it is information that helps Google to better understand the semantics, and on the other, the attractive and specific appearance of the SERP for that search can lead to more clicks, that is, increase CTR and visits.
Attributes rel dofollow / nofollow / ugc / sponsored
<a href="" rel="nofollow"> </a>Links on a website can be marked with the rel attribute to understand what the relationship of the link is to the website it points to.
For example, a link with a nofollow attribute does not transfer authority to the linked site, compared to the dofollow that does (or simply, if there are no attributes in the link, is considered dofollow by default).
Google also introduced other attributes such as ugc (links posted by users, such as links in comments and forums), and sponsored (to mark those links that are the result of a payment or commercial relationship that is not completely natural).
To analyze a website and monitor if the tags and other code elements are correctly implemented you can use a tool like Screaming Frog (paid), or free tools like Woorank, Seoptimer.
As you can see, the options are multiple, and they make the task much easier. However, you can always go to the web, right-click on it and click Inspect to see the code in pure format.
In this way, you will be able to see if you have the correct title and heading tags (h1, h2, h3, etc.), meta description, image alt, lang and hreflang language tags, open graph, twitter cards, canonical and other elements. HTML code required. You will also be able to see the Javascript codes (especially to check the insertions of scripts such as Google Analytics, Tag Manager and other external tools that you implement on the site).
Another alternative is to right click> View the source code of the page, and you will see all the code of the page (HTML, JS, CSS, etc).
What is the price of an SEO Audit? How much does it cost to audit a website?
The price of the SEO Audit depends on the size and difficulty of the project and the areas to be analyzed.
You can do a complete audit of a website, or you can audit specific aspects where there are suspicions that they are causing problems or that need improvement.
When calculating the price of the SEO Audit, you can ask yourself the following approaches.
- How long will it take depending on the specific difficulties that the project presents?
- What is the degree of difficulty that the diagnosis will have?
- How many URLs does the website you are going to audit have and how complex is its architecture?
- What will be the degree of detail and depth that you are going to apply in the study?
- What is the system or CMS that the web uses and its degree of difficulty?
- How many languages does the page have?
Given below are few experienced SEO professionals who can perform the SEO audit for you:
Any doubts or opinion?
Do leave a comment if you have any doubts. You can also contribute your point of view on how to do an SEO Audit, or tell us if you know other SEO tools, tricks, tips and anything that serves to enrich the content and thus we contribute among all






